


The following table presents a list of lattice energies for some common compounds as well as their structure type.ĭifference vs. It has been shown that neglect of polarization led to a 15% difference between theory and experiment in the case of FeS 2, whereas including it reduced the error to 2%. As an example, one may consider the case of iron-pyrite FeS 2. In these cases the polarization energy E pol associated with ions on polar lattice sites may be included in the Born–Haber cycle. Effect of polarization įor certain ionic compounds, the calculation of the lattice energy requires the explicit inclusion of polarization effects. The bond radii are similar but the charge numbers are not, with BaO having charge numbers of (+2,−2) and NaCl having (+1,−1) the Born–Landé equation predicts that the difference in charge numbers is the principal reason for the large difference in lattice energies.Ĭlosely related to this widely used formula is the Kapustinskii equation, which can be used as a simpler way of estimating lattice energies where high precision is not required. when ions are closer together the lattice energy increases (becomes more negative)īarium oxide (BaO), for instance, which has the NaCl structure and therefore the same Madelung constant, has a bond radius of 275 picometers and a lattice energy of −3054 kJ/mol, while sodium chloride (NaCl) has a bond radius of 283 picometers and a lattice energy of −786 kJ/mol.as the charges on the ions increase, the lattice energy increases (becomes more negative),.
The Born–Landé equation above shows that the lattice energy of a compound depends principally on two factors:
#Kcl lattice energy free
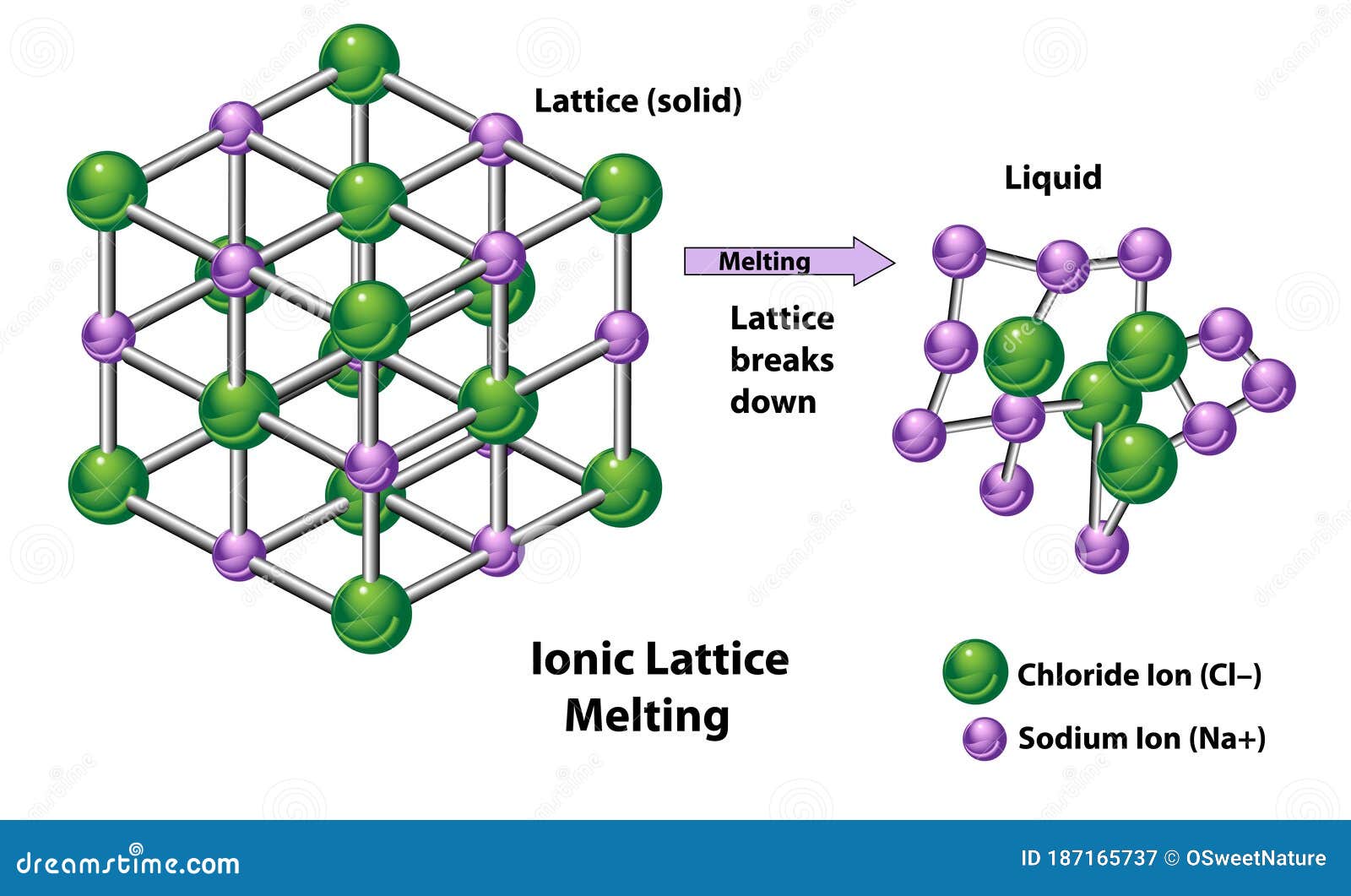
N A is the Avogadro constant M is the Madelung constant, relating to the geometry of the crystal z + is the charge number of the cation z − is the charge number of the anion e is the elementary charge, equal to 1.6022 ×10 −19 C ε 0 is the permittivity of free space, equal to 8.854 ×10 −12 C 2 J −1 m −1 r 0 is the nearest-neighbor distance between ions and n is the Born exponent (a number between 5 and 12, determined experimentally by measuring the compressibility of the solid, or derived theoretically). The relationship between the lattice energy and the lattice enthalpy at pressure P Following this convention, the lattice energy of NaCl would be +786 kJ/mol. as the energy required to convert the crystal into infinitely separated gaseous ions in vacuum, an endothermic process. Some chemistry textbooks as well as the widely used CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics define lattice energy with the opposite sign, i.e. In the case of NaCl, lattice energy is the energy change of the reaction The concept of lattice energy was originally applied to the formation of compounds with structures like rocksalt ( NaCl) and sphalerite ( ZnS) where the ions occupy high-symmetry crystal lattice sites. Lattice energy and lattice enthalpy Sodium chloride crystal lattice Since it generally cannot be measured directly, the lattice energy is usually deduced from experimental data via the Born–Haber cycle. The size of the lattice energy is connected to many other physical properties including solubility, hardness, and volatility. It is a measure of the cohesive forces that bind ionic solids. In chemistry, the lattice energy is the energy change upon formation of one mole of a crystalline ionic compound from its constituent ions, which are assumed to initially be in the gaseous state. Energy change upon the formation of one mole of ionic solid


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
