
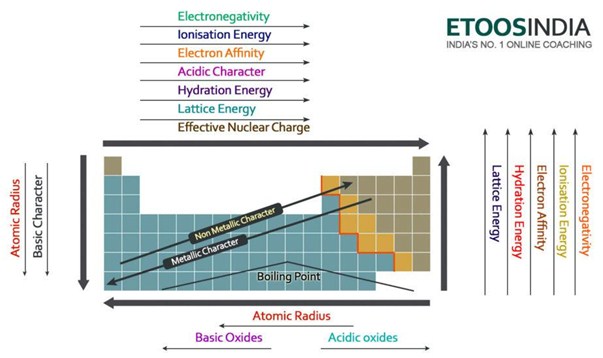
First look at the relative charges displayed by each ion in a given compound-if one compound has much higher ionic charges, then it will likely have the higher lattice energy.Ģ. Compare the results the largest quantity denotes the ionic compound with the largest lattice energy.ĭuring comparisons, we can also use the charge and distance variables to estimate relative lattice energies.Solve the equation for each ionic compound, inputting the charge and distance values specific to it.The final answer should be written in units of Joules (J). Q 1 & Q 2 = the relative charges of the constituent ions in an ionic compound We can summarize lattice energy periodic table trends in the following image:

More specifically, it increases from left to right across periods and from bottom to top up groups. To summarize, lattice energy increases as we increase ion charge and decrease the distance. Smaller ions produce larger lattice energies in their ionic compounds.
Essentially, larger ions compose ionic compounds with smaller lattice energies due to the increased distance between them. The distance between the constituent ions (represented by the variable R)Īs we increase the distance variable, lattice energy decreases. In turn, ions possessing weaker charges decrease the lattice energies of their compounds. This means that ions with larger charge values will produce ionic compounds with greater lattice energies. The charges held by the constituent ions (represented by the variables Q 1 and Q 2)Īs we increase the ion charge variable, lattice energy increases. Because this process requires energy, it falls into the endothermic category, corresponding to a positive value. On the other hand, if we use the alternate definition, the dissolution of an ionic compound, the nature of the lattice energy value changes. Our first definition, the formation of an ionic compound, involves exothermic lattice energy, corresponding to a negative value. A process is exothermic when it releases energy. We can view lattice energies as either endothermic or exothermic processes depending on which definition we focus on. Depending on our chosen definition, the lattice energy of a given ionic compound may either be a positive or negative value. Lattice energy can be described as a certain quantity of energy is released when gaseous ions react during the formation of one mole of a solid ionic compound however, it also describes the energy that facilitates the dissociation of one mole of a solid ionic compound into its constituent gaseous ions. These interactions involve large amounts of energy, explaining the high melting and boiling points characteristic of ionic compounds. Their strong, rigid composition enables interactions between each charged ion and its oppositely charged counterparts. The key to understanding this concept lies in the crystalline structure of ionic compounds. We can further investigate this term in two different ways, depending on our perspective. Lattice energy maintains the fixed positions of cations and anions within ionic compounds. Both the generation and dissolution of such compounds involve the concept of lattice energy, a type of potential energy expressed in units of kJ/mol. Topics Covered in Other Articlesĭuring the formation of solid ionic compounds, electropositive metals react with electronegative nonmetals.
LATTICE ENERGY TREND PERIODIC TABLE COMPOUNDS HOW TO
In this tutorial about lattice energy, we will cover its definition, relevant periodic table trends, factors that influence it, and how to calculate it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
